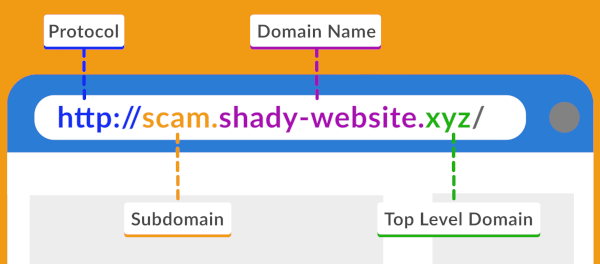
When browsing the web, using social media or checking your email, it is very important to exercise caution when clicking on links. Cybercriminals actively create deceptive links to infect devices with malware or steal personal information. Continue reading
Tag Archives: cybercriminals
8 Cyber Security Tips To Help Secure Your Business

Cyber security and Internet attacks has been all over the Australian media recently after the recent press conference from The Prime Minister – Scott Morrison. During the press conference, he mentioned that Australian Businesses, government agencies and other entities are under an active cyber attack campaign by a “state-based actor”. Scott didn’t elaborate too much on who they are but urged businesses to check and if needed increase their cyber security. Continue reading
How the Bad Guys Get Your Passwords
 Passwords are an essential part to your businesses cybersafety. If, like the rest of us, you have dozens of passwords to remember, you might take shortcuts. Taking advantage of this type of attitude is one way bad guys access your passwords. Continue reading
Passwords are an essential part to your businesses cybersafety. If, like the rest of us, you have dozens of passwords to remember, you might take shortcuts. Taking advantage of this type of attitude is one way bad guys access your passwords. Continue reading
How Hackers Attack Companies – Island Hopping
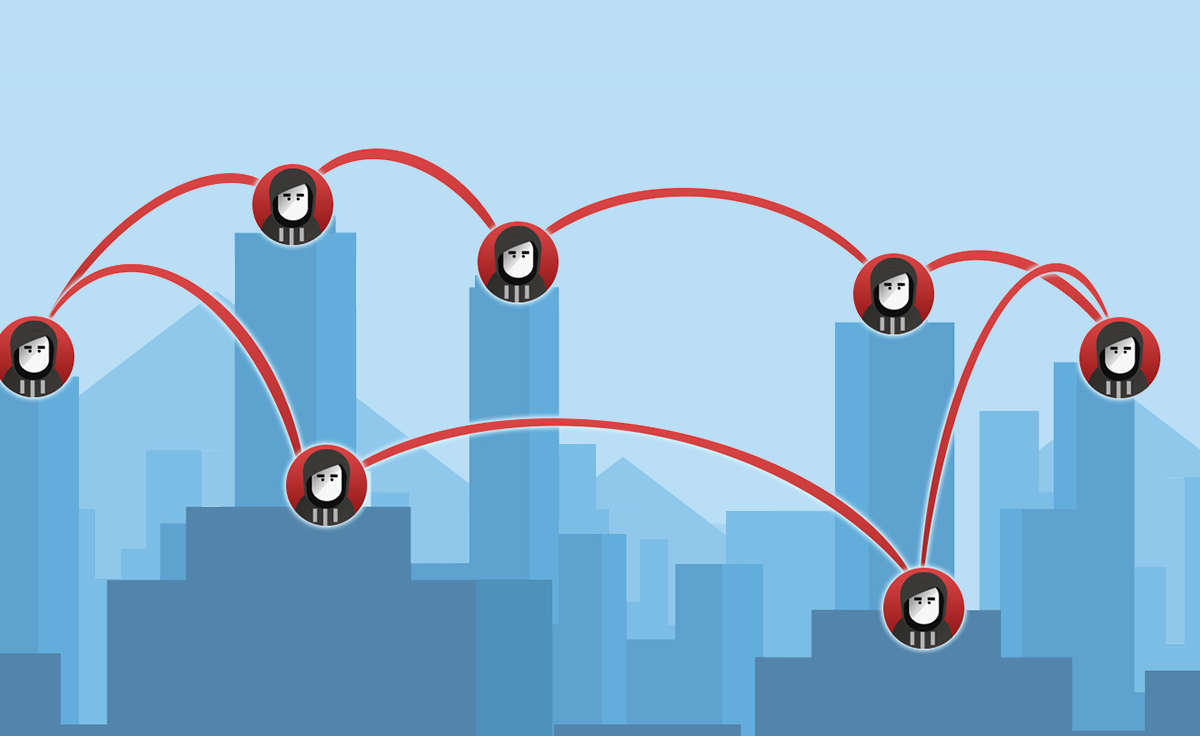
The phrase “island hopping” conjures up positive images of holidays, sandy beaches and cruises. But cybercriminals have given the term a new, less pleasant spin. Continue reading
Securing Your Business
Cybercrime has hundreds of millions of victims if not more! Two-thirds of people online have experienced personal information theft or compromise. A 2018 McAfee Security study suggested that represents more than 2 billion individuals! Continue reading
Think Before Clicking – 5 Red Flags of Phishing Emails
 Just one click can be the difference between maintaining computer security and suffering massive financial losses. All it takes is just one employee to click on a link in an email for your business to be vulnerable.
Just one click can be the difference between maintaining computer security and suffering massive financial losses. All it takes is just one employee to click on a link in an email for your business to be vulnerable.
Here are a list of 5 red flags that point out a potential phishing email:
1. Poor spelling and grammar
The occasional typo happens to even the best of us, an email filled with errors (both in grammar and spelling) is a clear warning sign of a phishing attempt. Most companies push their email campaigns through multiple reviews where errors are fixed and the language is refined. Errors throughout the entire message indicate that the same level of care was not taken and therefore the message is more than likely fraudulent.
2. An offer too good to be true
Free items or a lottery win sound great, but does the offer comes out of nowhere and with no catch? Then there is definitely cause for concern. Take care not to get carried away with the message and don’t click without investigating further.
3. Random sender who knows too much
Spear phishing is when an email or offer is designed and crafted especially for your business. Culprits take personal details from your public channels (Facebook, Twitter, Linkedin and even offline documents such as annual company reports etc) and then use it against you. The only clues? The sender is unknown – they weren’t at the event or involved in any way. Take a moment to see if their story checks out. Even check the email address of the sender to confirm that it is correct and not just a similar sounding or looking address (see #4 below).
4. The URL or email address is not quite right
One of the most effective techniques used in phishing emails is to use domains which sound almost right. For example, [microsoft.info.com] or [pay-pal.com] Hover over the link with your mouse and review where it will take you. If it doesn’t look right, or is completely different from the link text then delete the email.
5. It asks for personal, financial or business details
Alarms should ring when a message contains a request for personal, business or financial information. If you believe there may be a genuine issue, you can initiate a check using established, trusted channels (ie phone the person on their known number not one contained within the email).
While education is the best way to ensure phishing emails are unsuccessful, a robust spam filter and solid anti-virus system provide peace of mind that your business has the best protection available.
DP Computing can help secure your business and can even organise a fake phishing attack to see if further staff training is required. Give us a call to discuss how we can help you on 08 8326 4364 or
su*****@dp*********.au
.
Should You Pay for a Ransomware Attack?
 Getting hit with a ransomware attack is not fun, cybercriminals encrypt your data and you are left having to decide: should we pay to get them back? It is a scene that’s played out across the world with 70% of businesses saying “yes” in 2016 alone. Here are six factors to consider if you are ever in this situation.
Getting hit with a ransomware attack is not fun, cybercriminals encrypt your data and you are left having to decide: should we pay to get them back? It is a scene that’s played out across the world with 70% of businesses saying “yes” in 2016 alone. Here are six factors to consider if you are ever in this situation.
1) Do you trust them?
Remember that they are criminals holding your data hostage, how confident are you that they will send you the decryption key and that the key will decrypt all your data? The attackers demand you send the payment via untraceable Bitcoin, so you have no recourse if you never hear from them again. You are also equally trapped if they decide to come back with increasingly higher demands. If they do send the decryption key, be aware they still have access to your systems and can hit you again at any time until your network is fixed by experts. Businesses don’t exactly want their breach publicised, so many don’t admit to paying the ransom, whether it went to plan or otherwise.
2) Can you manage the impact?
The best case scenario is that you can wipe the affected drives and restore from a clean backup without paying the ransom. You may even decide that the encrypted files aren’t that important and simply let them go and just wipe the infected machine. On the other hand, if your data management comes under any special regulations, like health or legal, you may find that the attack has a much wider impact. The attacker will also motivate you to pay the ransom quickly with a countdown and a threat of total deletion when it hits zero. Remember that if the data isn’t that valuable, or you have confirmed backups, this urgency should have no effect on your plans. T
3) How much do they want?
Cybercriminals rarely send out attacks with set amounts, instead, they prefer to customize the ransom based on how much they think you can pay. Large corporations and hospitals are hit with very high demands, while small business demands are more modest. Different countries or regions are also charged differing amounts. They may be “bad guys”, but they are smart people who know your financial limits. They also consider how much similar businesses have paid previously and expect you to follow suit.
4) Are your backups any good?
Always check your backup to confirm that they are working, that the correct data is being backed up and that you can recover the data from them. Many businesses are discovering too late that their backup systems are not robust enough. Either the backup has become infected too, they weren’t up-to-date or they backed up the wrong data. It is imperative that you at least do some quick backup checks to ensure you can recover all your data in case the unfortunate happens.
5) What are you policies?
Businesses are now adding ransomware to their disaster recovery plans and have predefined actions mapped out. Seemingly simple inclusions like who has final say over the payment decision can stop chaos in its tracks. Employees and management alike can then approach the situation calmly and make the best decisions for the business.
6) Stay safe in the first place
Ransomware is not slowing down and all factors say it will increase. As more businesses pay the ransom the cybercriminals are steadily launching new attacks and making it their full-time job. Most of the attacks come via phishing emails – those emails that trick employees into clicking a link – and they can be extremely convincing. While training staff helps, it’s no guarantee. We recommend using business-class spam filters to catch these types of emails before they land in your inboxes so that triggering a ransomware attack becomes something that happens to other businesses and not yours.
Secure your data systems and check your backups now. If you need help, contact us on 08 8326 4364 or
su*****@dp*********.au
.